 |
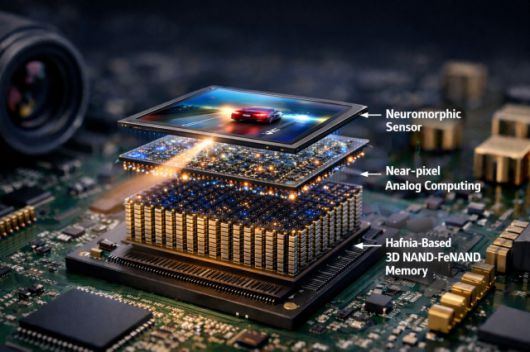
This AI_generated image shows a chip capable of thinking like humans by analyzing visual information. Courtesy of KAIST |
<이미지를 클릭하시면 크게 보실 수 있습니다> |
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) announced on December 31, Wednesday, that a research team led by Professor Chon Sang-hun from the School of Electrical Engineering presented six papers at the International Electron Devices Meeting (IEEE IEDM 2025) in San Francisco. The team work on integrated vision sensors was selected as a "Highlight Paper," and their research on highly reliable memory received the "Top Ranked Student Paper" award.
Standard AI systems function like a relay race: a camera sensor takes a picture, converts it into numbers, moves those numbers to memory for storage, and then sends them to a processor to be calculated. This constant moving of data back and forth uses a lot of electricity and creates a "lag" in response time. The KAIST team solved this by creating a "full-stack" AI chip where the sensor and the brain-like processing circuits are physically stacked on top of each other in very thin layers.
This "in-sensor" technology allows the chip to "see and think" at the same time. Instead of sending raw data elsewhere, the sensor itself performs the calculations. This mimics how the human nervous system processes basic visual features before the information even reaches the deep brain. By eliminating the need to move data between different chips, the system uses significantly less power and reacts much faster, making it ideal for real-time use in mobile devices, drones, and robots.
In addition to the sensing technology, the team improved the storage part of the AI chip. They developed a new type of memory called "Next-Generation NAND Flash" that uses a special material to store data more reliably while using lower voltage. This ensures that the AI can store vast amounts of information safely for a long time without draining the battery.
Professor Chon Sang-hun stated that this research proves that sensors, computation, and storage—which used to be designed separately—can be combined into one single system and material. He noted that this platform will be expanded for use in "edge AI," which refers to smart devices that need to process complex information locally and instantly without relying on a central server.
The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. It was conducted in collaboration with Samsung Electronics, Kyungpook National University, and Hanyang University.
(Paper information)
Journal: IEEE IEDM 2025 Title: Monolithically Integrated Photodiode–Spiking Circuit for Neuromorphic Vision with In-Sensor Feature Extraction DOI: https://iedm25.mapyourshow.com/8_0/sessions/session-details.cfm?scheduleid=255
Title: A Highly Reliable Ferroelectric NAND Cell with Ultra-thin IGZO Charge Trap Layer; Trap Profile Engineering for Endurance and Retention Improvement DOI: https://iedm25.mapyourshow.com/8_0/sessions/session-details.cfm?scheduleid=124
Park Sae-jin Reporter swatchsjp@ajunews.com
- Copyright ⓒ [아주경제 ajunews.com] 무단전재 배포금지 -
이 기사의 카테고리는 언론사의 분류를 따릅니다.
기사가 속한 카테고리는 언론사가 분류합니다.
언론사는 한 기사를 두 개 이상의 카테고리로 분류할 수 있습니다.
언론사는 한 기사를 두 개 이상의 카테고리로 분류할 수 있습니다.